2021
Type of resources
Available actions
IADC Research Activities
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Representation types
Update frequencies
status
Scale
-
Brief narrative summary of the content of the resource(s)
-
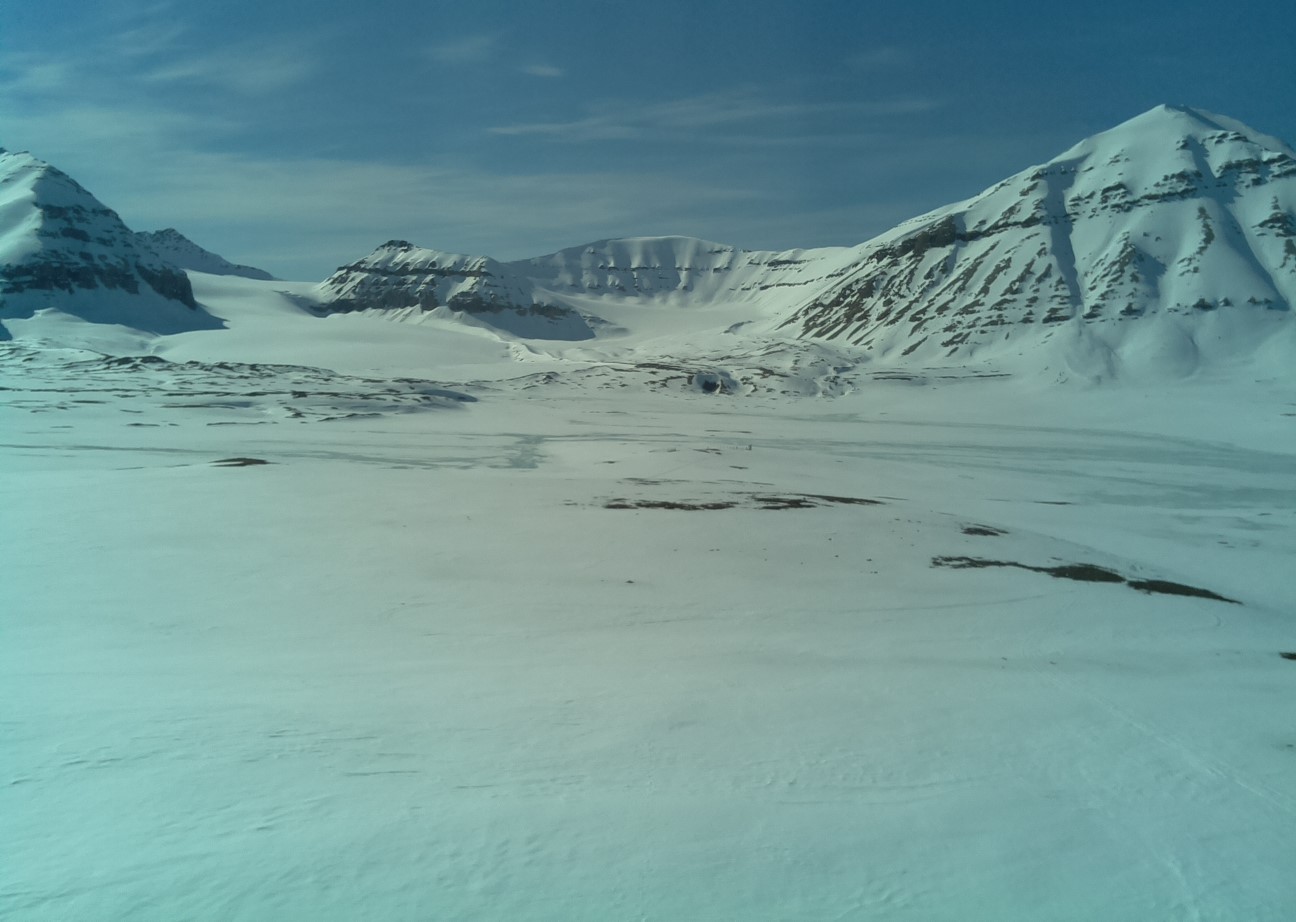
Atmospheric Gondola for Aerosol Profiles (AGAP) The scientific goals of AGAP are to develop novel aerosol payloads and evaluate the vertical distribution of aerosol properties in the Arctic Boundary Layer. Dataset consists in Aerosol vertical profiles gridded at a 50 m spatial resolution: R, T, P, RH, Aerosol size distribution, BC concentration, O3. Maximum altitudes 1500 m.
-
Atmospheric Gondola for Aerosol Profiles (AGAP) The scientific goals of AGAP are to develop novel aerosol payloads and evaluate the vertical distribution of aerosol properties in the Arctic Boundary Layer. Dataset consists in Aerosol vertical profiles gridded at a 50 m spatial resolution: R, T, P, RH, Aerosol size distribution, BC concentration, O3. Maximum altitudes 1500 m.
-
Snow sampling every week near Gruvebadet (Svalbard)
-

Terrestrial Photography ApplicationS on Snow covEr in Svalbard (PASSES) Project start: 2018-04-15 - end: 2021-12-31 The purpose of this activity is the development of a new snow product focused on the estimation of the fraction of snow cover in selected sites at different spatial resolutions. This dataset will be aimed to support the estimation of cryospheric information using remotely sensed data, with a particular attention to data obtained in the framework of the Copernicus program. The availability of this dataset in a natural laboratory such as Svalbard islands will support the reduction of the gap between remotely sensed data and modeling activities. This added value will be very important considering the higher spatial resolution of the sensors recently deployed. The dataset will be based on re-using data obtained from public repositories such as the digital elevation model of Svalbard, the available webcam imageries in Svalbard and satellite products from Landsat, Sentinel and MODIS missions. All the available data will be integrated in order to estimate the fraction of snow cover, at different spatial resolutions, for each satellite mission. These estimations, computed at different sites in Svalbard islands, will offer the opportunity to better integrate results obtained by remote sensing with modeling and air-snow interactions studies. Particular attention will be devoted to the formalization of agreements with raw-data providers in case of not-public licensing policies.
-

The column water vapor or Precipitable Water Vapor (PWV) is measured at Thule Air Base (76.5°N, 68.8°W), Greenland, by means of a ground-based millimeter-wave spectrometer (GBMS) installed at 220 m a.s.l. The GBMS observes rotational lines of atmospheric molecules emitting between 230 and 280 GHz, with a spectral pass band of 600 MHz. The PWV is calculated from direct measurements of atmospheric opacity (tau) at the indicated frequencies by using the linear relation PWV = a+tau*b, where a and b depend only on frequency. Measurements have a temporal resolution of 15 minutes and are carried out continuously when the GBMS is operated.
-

This proposal will focus on eutrophication, contaminants, marine litter and underwater noise descriptors of the MSFD. Vertical acquisition in 18 CTD station in Kongsfjorden with water sampling at 2-3 depths (surface, intermediate, bottom) for nutrient and pH analyses of sampled water in the lab
-
Isotopic characterisation of arcic ponds Sampling of ponds and surrouding terrestrial envionrment. matter (expressed as ash fry dry matter) and N content as a percentage in soil and lake sediment.
-

Permafrost Release Into The Marine System In A Warming Arctic (PRIMA) Data about Physical and chemical oceanography and vertical fluxes of sedimentary material from Mooring Aldo Pontremoli (MAP) and geochemical biomarker data from sediment core. Instrument: SBE56, SBE37, Sediment trap Technicap PPS 4/3, GC-MS
-

Monitoring of Aerosol: Short and Long range source areas related to Climate Change (MAShLoCC) During the Arctic campaign 2010, an atmospheric aerosol sampling at the Gruvebadet observatory has been carried out in order to obtain information about the formation and composition of atmospheric aerosol, transport processes toward the Arctic zone as well as local and remote source areas. Instrument : ICP-SFMS, IRMS, Orbitrap