CNR-ISP
Type of resources
Available actions
IADC Research Activities
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Representation types
Update frequencies
status
Scale
-
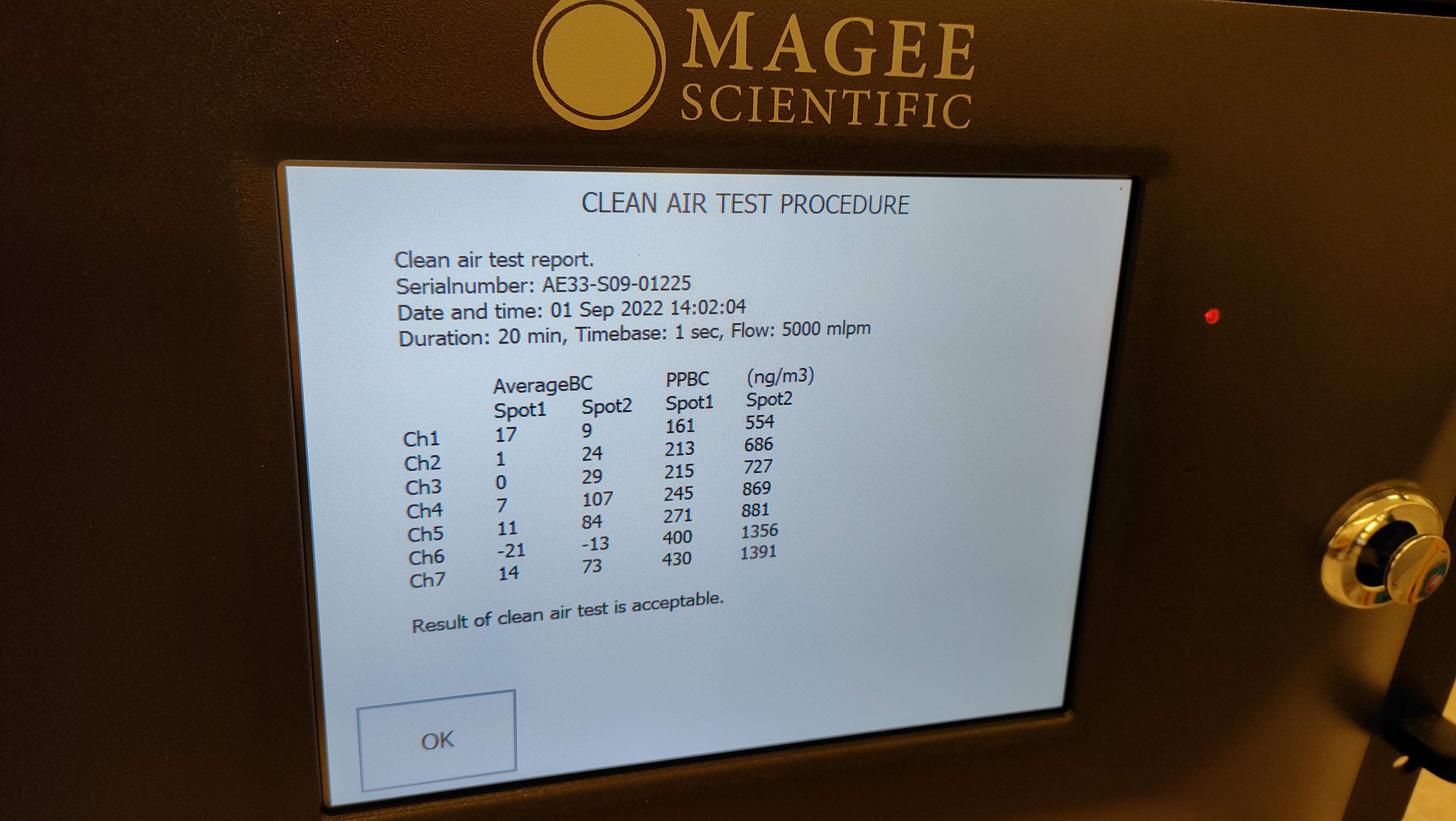
Aerosol scattering coefficient at 1 wavelength (530 nm) measured using a nephelometer M903 manufactured by Radiance Research and absorption coefficient at 7 wavelengths (370, 470, 520, 590, 660, 880, 950 nm) measured using an AETHALOMETER AE33 from Aerosol Magee Scientific.
-
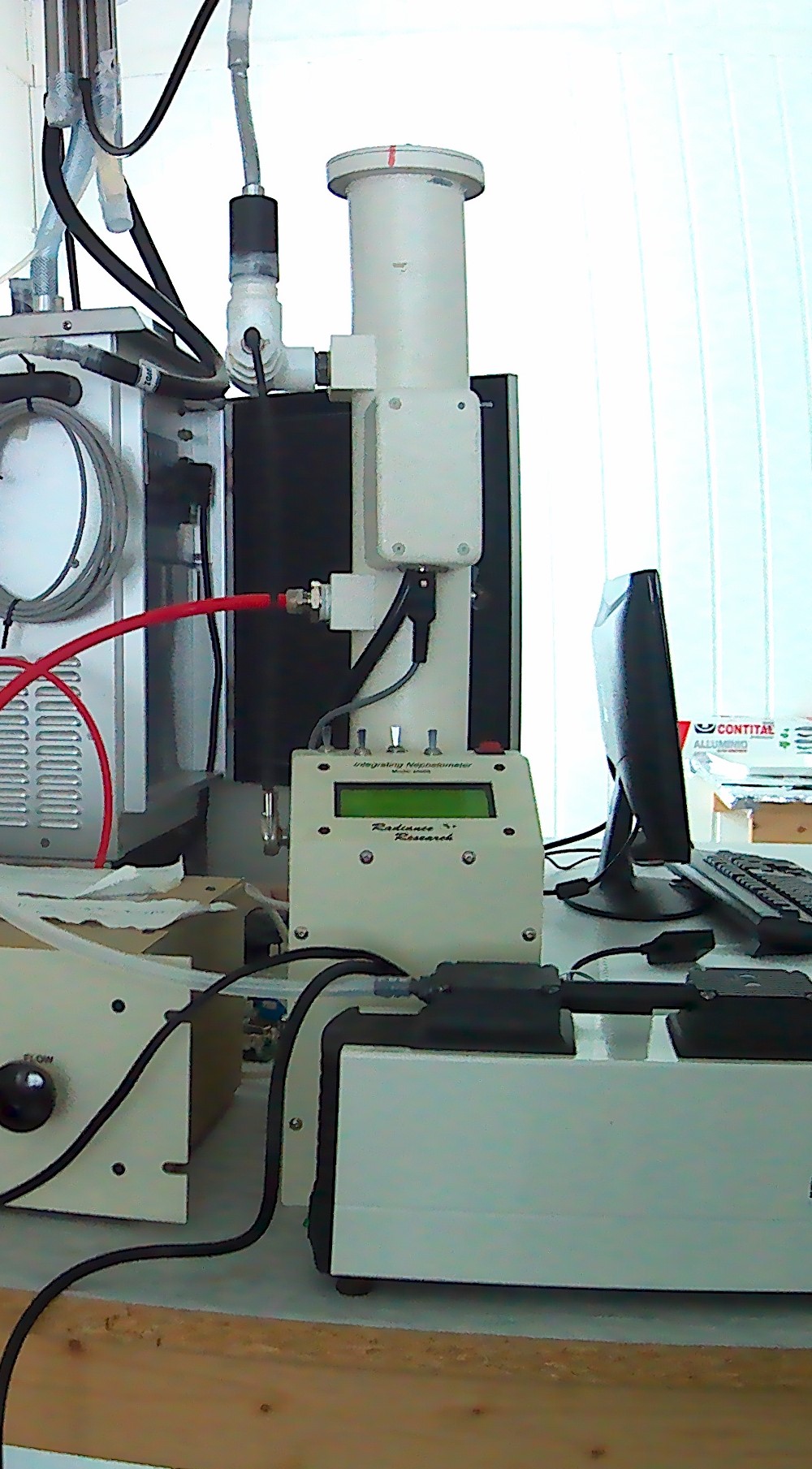
Aerosol scattering coefficient at 1 wavelength (530 nm) measured using a nephelometer M903 and absorption coefficient at 3 wavelengths (467, 530, 660 nm) measured using a Particle Soot Absorption Photometer (PSAP), both manufactured by Radiance Research.
-
Mixing state and organic volume fractions of sub micron aerosol particles collected at the Zeppelin observatory
-

RIS: 3471 ARCA aims to develop a conceptual model on the mechanism(s) behind the release of large volumes of cold and fresh water from melting of ice caps, investigating this complex system from both paleoclimatic and modern air-sea-ice interaction process point of view. ARCA fits well within the Italian Strategy for Arctic. Testing and calibration of sensors measurement of vertical profile of turbulence, meteorological paramaters and characterisitic of the snow surface.
-
Daily averages of equivalent black carbon from aerosol absorption coefficient at 660nm measured using a Particle Soot Absorption Photometer (PSAP), manufactured by Radiance Research. MAC equal to 10 m^2/g.
-
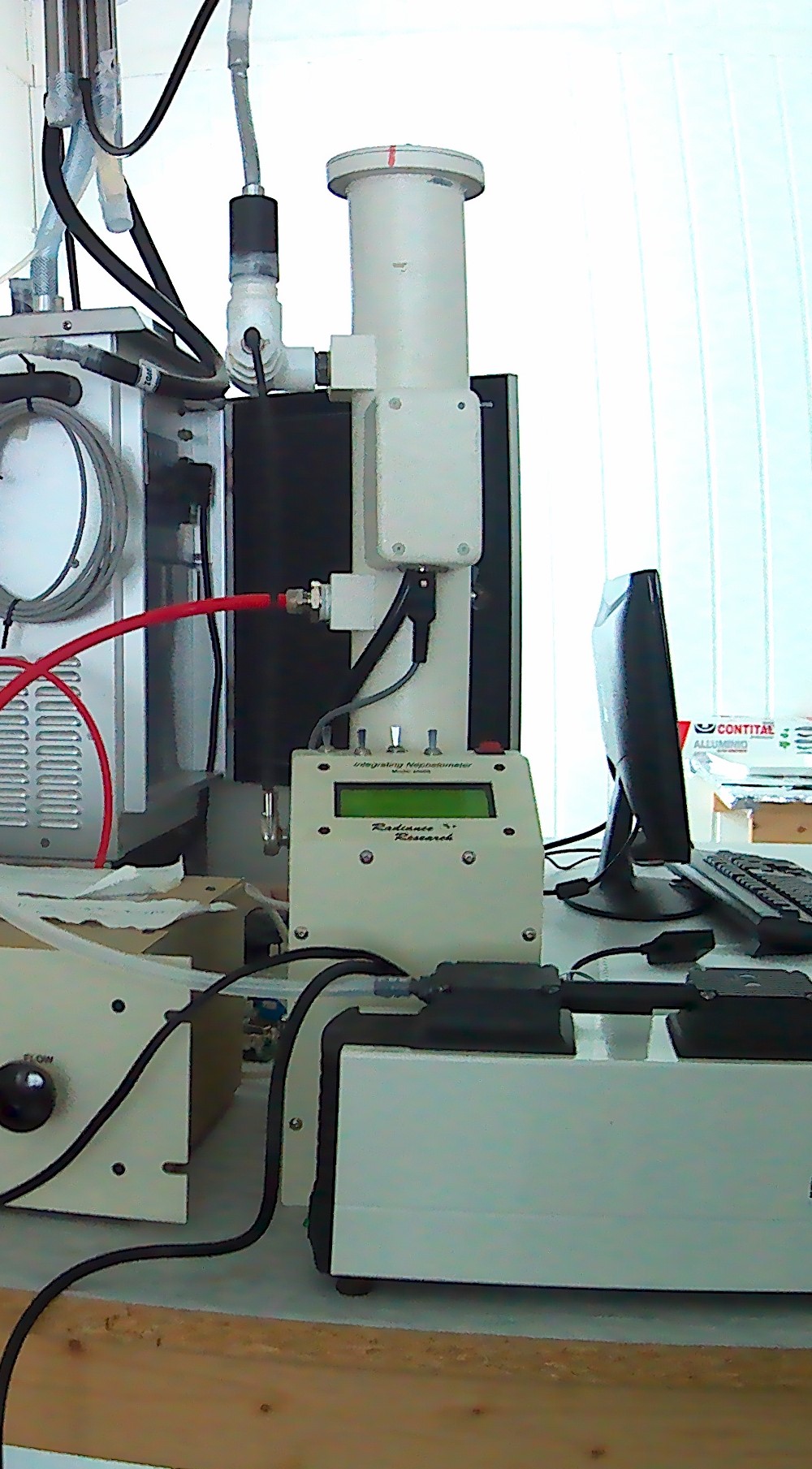
Aerosol scattering at 1 wavelength (530 nm) measured using a nephelometer M903, manufactured by Radiance Research.
-
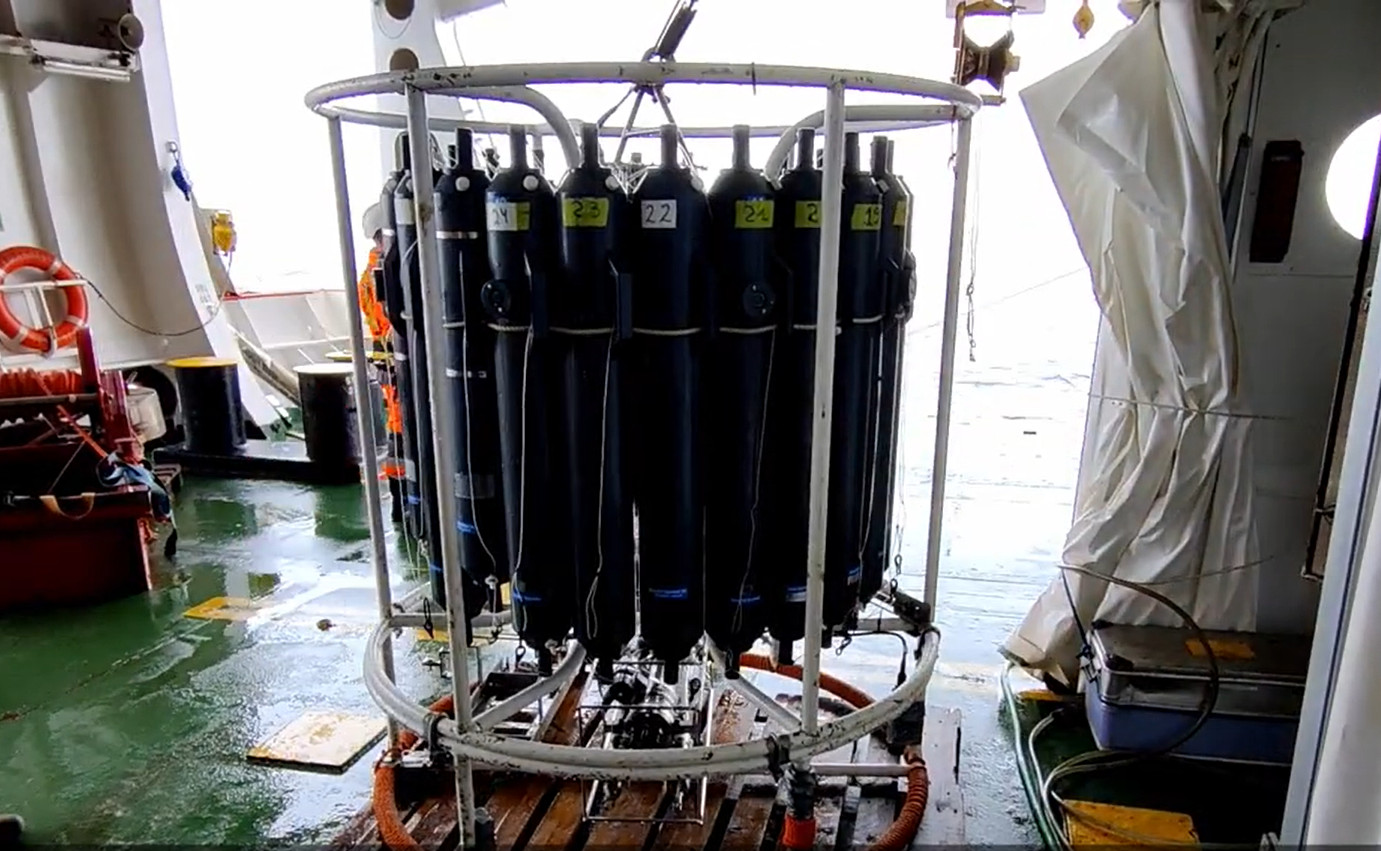

The Italian project CASSANDRA is part of the international framework of the Synoptic Arctic Survey which seeks to collect oceanographic data in the Arctic Ocean in the two-year period 2020-2021 involving the coordination of many research vessels belonging to different nations. The aim is to determine the current state and major ongoing changes in the Arctic marine system by generating an oceanographic dataset that allows for a comprehensive characterization of Arctic hydrography and circulation, carbon uptake and ocean acidification, the distribution of possible pollutants, the functioning and productivity of organisms and ecosystems.
-
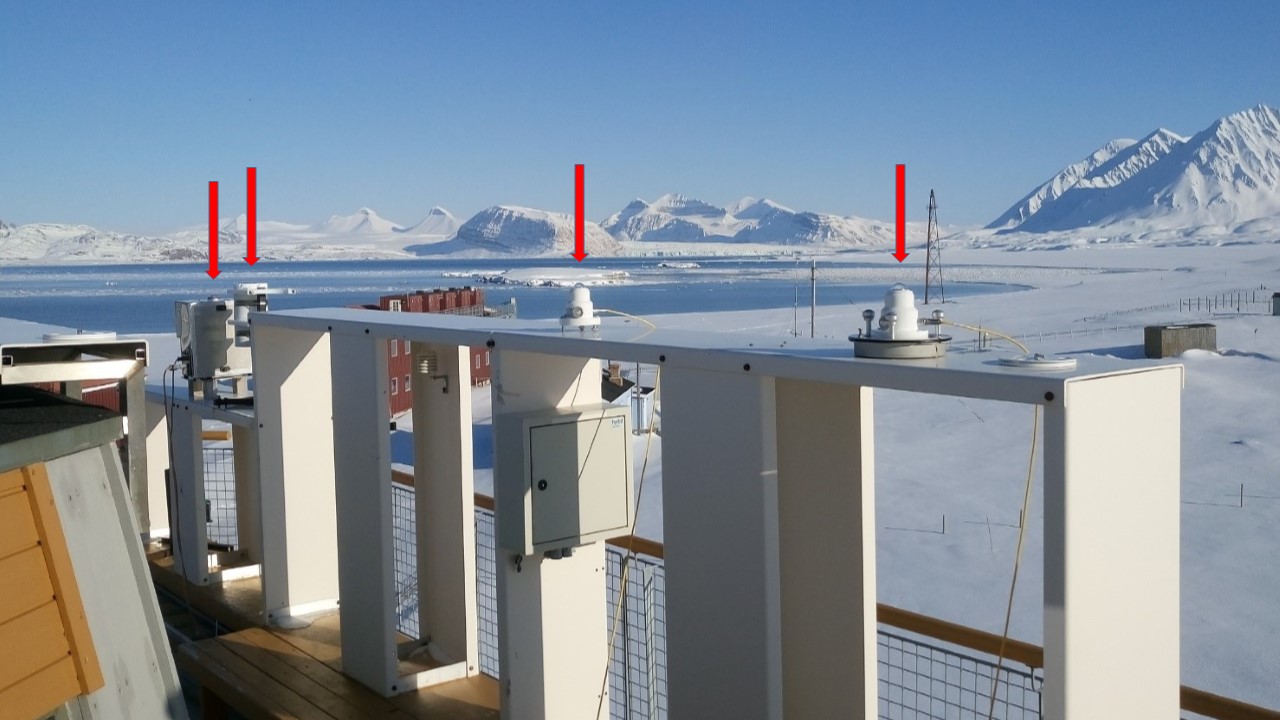

The main goal of the UV-ICARE project was to establish a network of UV-monitoring stations on Svalbard, which is optimally coordinated and homogenised. This implies harmonization of operational routines, data analysis and storage, including a thorough instrument inter-comparison. The latter was a central element of activities. In the inter-comparison campaign that took place in Ny-Ålesund from 17 to 23 April, 2018 participated (from left to right in the photo): 1.Narrow-band filter radiometer UV-RAD, managed by the Institute of Polar Science at the National Research Council, Italy (CNR-ISP). The instrument measures the erythemally weighted solar UV irradiance (UVE) and ozone column at Ny-Ålesund. 2.Filter GUV radiometer, produced by Biospherical Instr., operating under responsibility of the Norwegian Institute for Air Research (NILU). The radiometer provides solar UVE irradiance and ozone column at Ny-Ålesund. 3.Kipp & Zonen UVS-AE-T radiometer that measures UVE irradiance and operates at Hornsund station under responsibility of the Institute of Geophysics at the Polish Academy of Sciences (IGF-PAS). 4.Kipp & Zonen UVS-E-T radiometer that also provides solar UVE irradiance and works at Longyearbyen station, under management of Masaryk University (MU), Brno and University of South Bohemia (USB), Czech Republic. 5.Brewer #050 spectroradiometer (shown in the second picture) that provided UVE irradiance and ozone column as a reference instrument. The devise operates at Ny-Ålesund under responsibility of CNR-ISP. The inter-comparison resulted in very good agreement (±5 %) of the instruments involved, over most of solar zenith angles and weather conditions sampled, despite different technical specifications. On the basis of this campaign, it can be stated that all measurements in Ny-Ålesund, Hornsund and Longyearbyen are directly comparable at solar zenith angles < 80°. Partly funded by Arctic PASSION project (agreement number 101003472).
-
Snow sampling every week near Gruvebadet (Svalbard)
-
Aerosol absorption coefficient at 3 wavelengths (470, 530, 670 nm) measured using a Particle Soot Absorption Photometer (PSAP), manufactured by Radiance Research.