Type of resources
Available actions
IADC Research Activities
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Representation types
Update frequencies
status
Scale
-
Snow sampling every week near Gruvebadet (Svalbard)
-

The Climate Change Tower Integrated Project (CCT-IP) reflects the priorities of Italian Arctic research and aims to investigate the interactions among all components of the Arctic climate system. The Amundsen-Nobile Climate Change Tower (CCT) serves as the project’s central infrastructure, providing continuous measurements of atmospheric parameters at multiple heights and at the critical interface between the surface and the atmosphere. A SPN1 net radiometer, installed at a height of 33 m in 2023, is used to measure the radiation partition between incoming direct and diffuse irradiance. Previously, in 2009, a combination of sensors—including a CNR1 net radiometer at 33 m and CM11 and CG4 sensors at 25 m—was deployed for the same purpose. Radiation data are processed to provide 30-minute averages (μ) and standard deviations (σ), along with derived products such as total net radiation and an indication of sun presence. These data will be available for download. Additionally, 1-minute resolution data are available for download upon request.
-
Snow sampling every year at the Kongsvegen glacier, in Svalbard
-
This dataset comprises measurements from moored Acustic Doppler Current Profiler (ADCP), collected by the S1 Mooring, which is managed by the Institute of Polar Sciences of the National Research Council (CNR) and National Institute of Oceanography and Applied Geophysics (OGS). The data was gathered on the Fram Strait south of the Spitsbergen in an open-sea area strongly influenced by both the interaction between Atlantic (northward-moving) and Arctic (southward-moving) waters as well as by the presence and winter formation of sea ice and atmospheric forcing. The easternmost part of the Fram Strait, relatively warm and salty Atlantic waters flow, bringing heat to the Arctic region and contributing to the Atlantification phenomenon. The processes responsible of the inter-annual and seasonal variability of the deep current flow in this open sea region are still unknown and also what the implications are related to ongoing climate change and in particular to the progressive decrease of sea ice cover in the winter period. To understand these dynamics, a deep-water oceanographic S1 Mooring was anchored at about 1040 meters depth, since June 2014. The dataset is also part of the SIOS-Svalbard Integrated Arctic Earth Observing System, developed to observe the impacts of climate change, including the rapid loss of sea ice cover, the retreat of local glaciers, and the Atlantification of Arctic seas. The ADCP mounted at 420 m measure: sea-water currents intensity and direction along the water column. The acquisition of this time series data is still ongoing and will continue, bolstered by the inclusion of this infrastructure within the framework of the Italian PNRR project ITINERIS. This ensures sustained data collection and further enhances our understanding of the observed environmental changes.
-
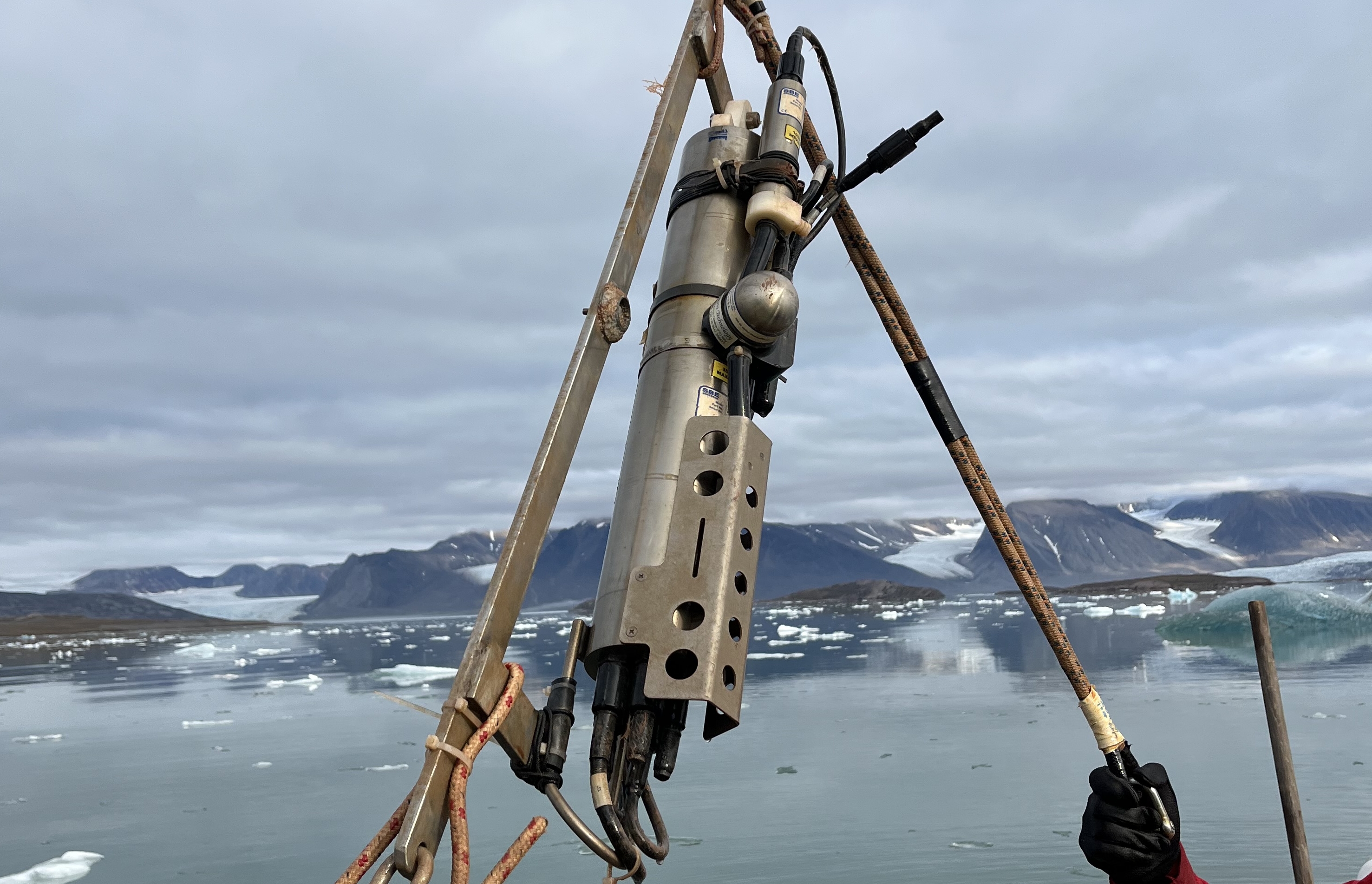

This dataset comprises measurements from moored CTD instruments, collected by the Mooring Dirigibile Italia (MDI), which is managed by the Institute of Polar Sciences of the National Research Council (CNR). The data was gathered at Kongsfjorden, Svalbard Island, since 29 May 2016 . This dataset is also part of the SIOS-Svalbard Integrated Arctic Earth Observing System, developed to observe the impacts of climate change, including the rapid loss of sea ice cover, the retreat of local glaciers, and the Atlantification of Arctic seas. Measured properties are: sea-water pressure, temperature, potential temperature, practical salinity, density, turbidity, fluorescence, PAR and dissolved oxygen in sea-water. The acquisition of this time series data is still ongoing and will continue, bolstered by the inclusion of this infrastructure within the framework of the Italian PNRR project ITINERIS. This ensures sustained data collection and further enhances our understanding of the observed environmental changes.
-
Brief narrative summary of the content of the resource(s)
-
The Climate Change Tower Integrated Project (CCT-IP) represents the guide lines of the italian research in the arctic and aims to study the interaction between all the components of the climate system in the Arctic. The Amundsen-Nobile Climate Change Tower (CCT) is the key infrastructure of the project, and provides continuous acquisition of the atmospheric parameters at different heights as well as at the interface between the surface and the atmosphere. Images of the sky are taken every 15 minutes and are available under request.
-
pH tipping point in Svalbard (pHinS) The project is focused on carbonate chemistry in the fjord and measure how meltwater, icebergs and freshwater runoff affects the acidity of coastal seawater. Acquisition of CTD profiles and seawater samples at discrete depths (surface, bottom and 1-3 intermediate depths) to determine pH, total alkalinity, dissolved inorganic carbon, dissolved oxygen, nutrients, dissolved organic carbon. Collection of samples from icebergs and streams to determine the same set of parameters measured in the seawater. Some of the analysis were performed in the laboratory of the “Dirigibile Italia” Arctic station soon after the collection; others will be performed on preserved samples in ISMAR’s laboratories. 62 water column profiles of pressure, Temperature, salinity, dissolved oxygen, turbidity instrument: SBE19plus
-

The Climate Change Tower Integrated Project (CCT-IP) represents the guide lines of the italian research in the arctic and aims to study the interaction between all the components of the climate system in the Arctic. The Amundsen-Nobile Climate Change Tower (CCT) is the key infrastructure of the project, and provides continuous acquisition of the atmospheric parameters at different heights as well as at the interface between the surface and the atmosphere. Surface-atmosphere interface data include heat-flux between soil and snow and into the soil, soil temperature and snow skin temperature. 30 minutes average (μ) and standard deviation (σ) will be available for the download. Data at resolution of 1 minute are available for online visualization and downloadable under request. Partly funded by Arctic PASSION project (agreement number 101003472).
-

This dataset comprises measurements from moored surface buoy installed in Kongsfjorden in the port of NyAlesund. The buoy is managed by the Institute of Polar Sciences of the National Research Council (CNR). The buoy was deployed in June 2025 with the aim to expand the observation on the sea-surface layer and also on the athmosphere in the framework of the Italian PNRR project ITINERIS. The buoy is equipped with meteo station and underwater sensors to measure physical properties of the athmosphere and biogeochemical properties of the surface layer.