oceans
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Representation types
Update frequencies
status
Scale
-

Permafrost Release Into The Marine System In A Warming Arctic (PRIMA) Data about Physical and chemical oceanography and vertical fluxes of sedimentary material from Mooring Aldo Pontremoli (MAP) and geochemical biomarker data from sediment core. Instrument: SBE56, SBE37, Sediment trap Technicap PPS 4/3, GC-MS
-
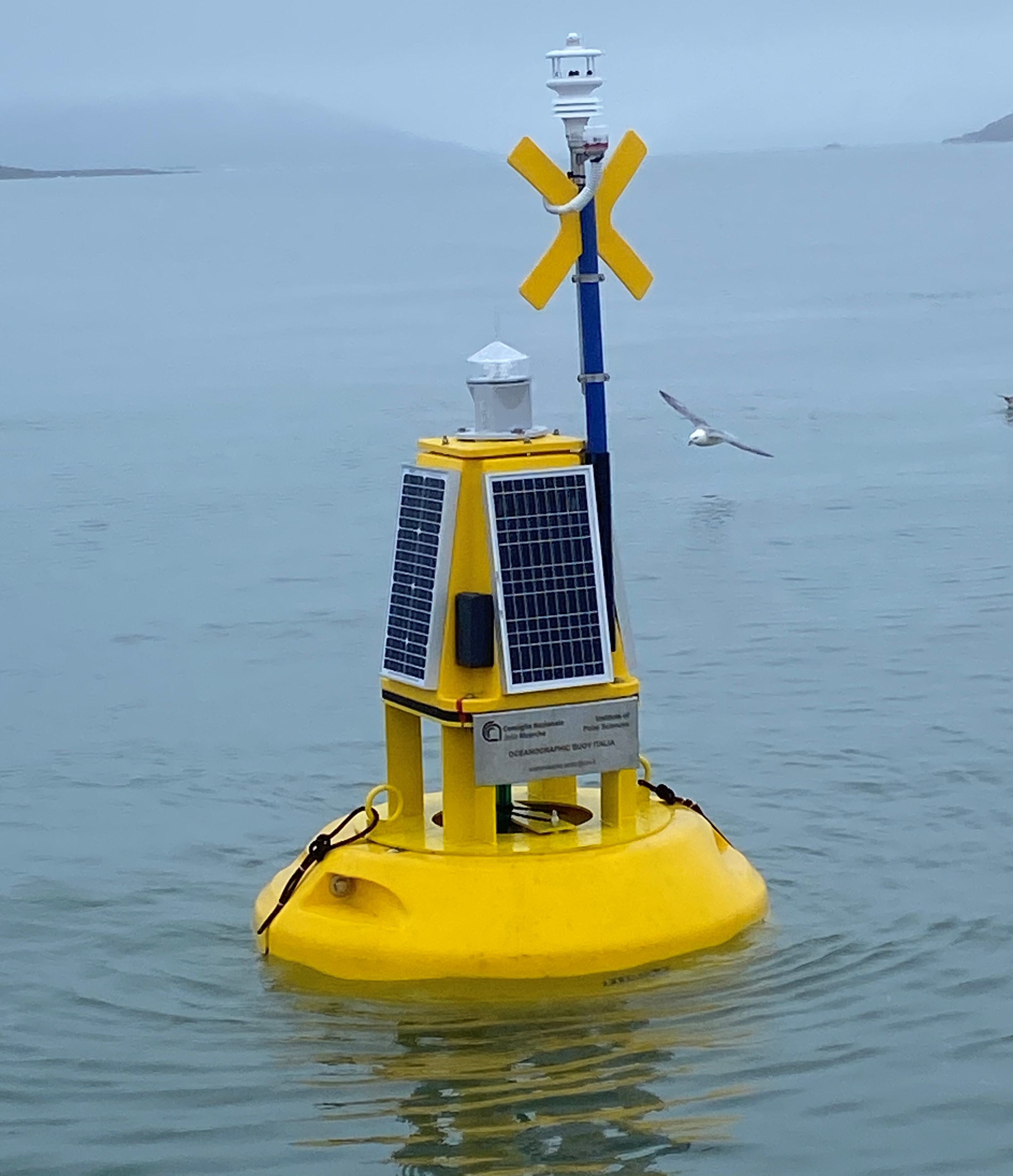

This dataset comprises measurements from moored surface buoy installed in the Kongsfjorden in proximity of the Mooring Dirigibile Italia (MDI). The buoy is managed by the Institute of Polar Sciences of the National Research Council (CNR). The buoy was moored in September 2023 with the aim to expand the observation on the sea-surface layer and also on the athmosphere in the framework of the Italian PNRR project ITINERIS. The buoy is equipped with sea surface temperature sensor positioned at 1m below the sea-level and meteorological station mounted at 2 m above the sea-leve. Mesured properties are seawater temperature, wind speed and direction, air pressure, air temperature, solar radiation and atmospheric humidity.
-
ISotopic and physical-chemical MOnitoring of GLACial drainages and sea water in the Ny-Ålesund area (Svalbard) The dataset includes vertical profiles of physical-chemical performed on-site in different sites along the fjord in Kongsfjorden.
-
DOC fractionation: dynamic of POPs and trace metals Arctic DOC (ArcticDOC) The sampling design is projected to cover almost five sampling points in the Kongsfjorden. The sampling of surface water (approximately 100 liters for each sampling point) and sediment are aimed at the determination of persistent and emerging contaminants: POPs PFAS, CUPs, PPCPs, endocrine disruptors such as nonylphenols and bisphenol A. At the same time, with tangential-flow ultrafiltration, dissolved organic matter (DOM) will be characterized according to size fractions (colloidal and truly dissolved) and the distribution of contaminants associated to these fractions will be evaluated.
-
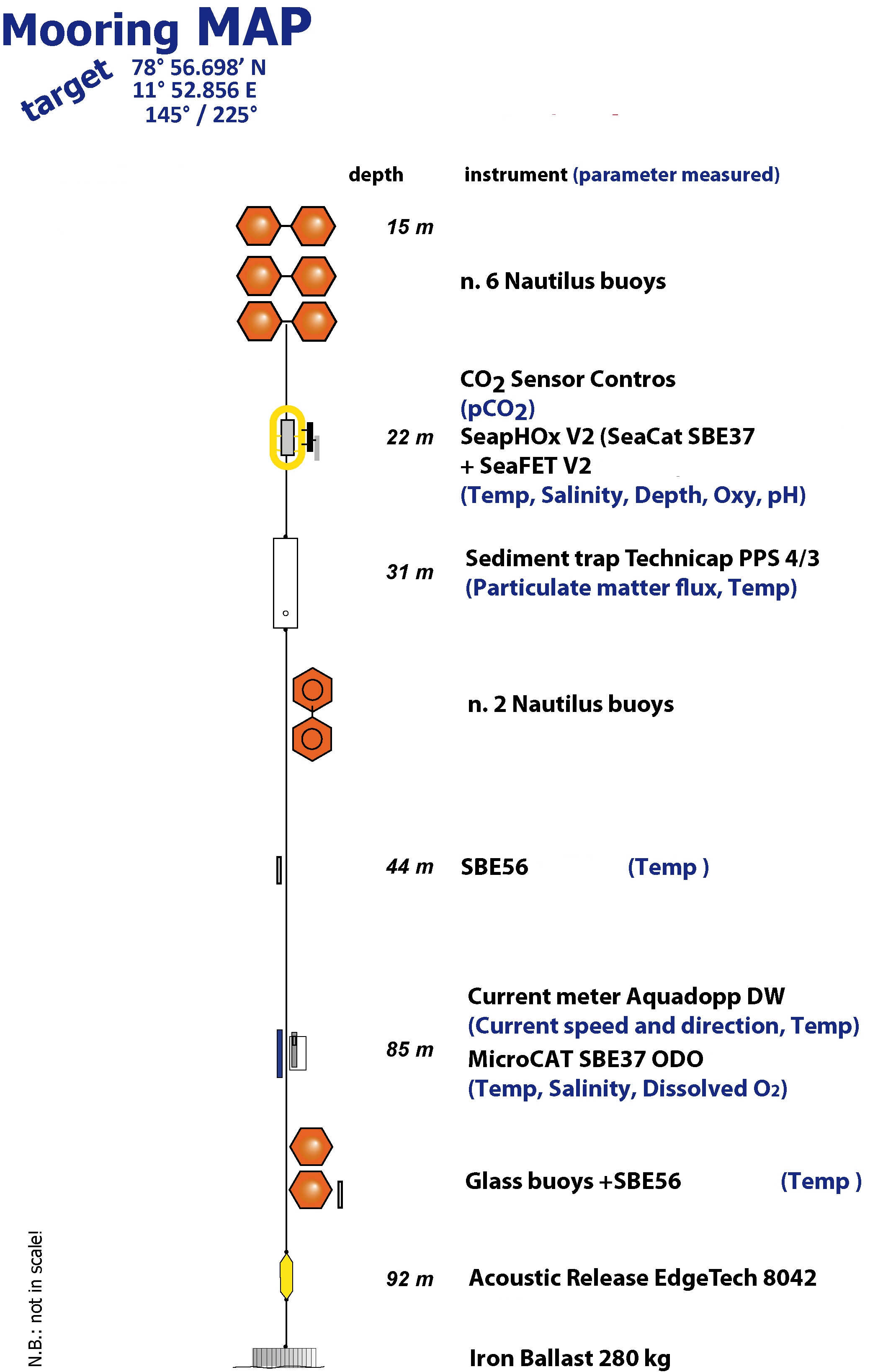
The Aldo Pontremoli Mooring (MAP), operated by the Institute of Polar Sciences of the National Research Council (CNR), has been active in the Kongsfjord, located in the Svalbard archipelago, since September 11, 2020. It is situated near the mouth of Bayelva River mouth and is influenced by land terminating glaciers and the release of permafrost. Currently, the mooring line is equipped with various instruments positioned at depths ranging from 22 to 97 meters within the water column. These instruments collect a wide array of physical and biogeochemical Essential Ocean Variables, including seawater pressure, temperature, conductivity, salinity, currents, dissolved oxygen concentration, pH, particle fluxes and dissolved carbon dioxide concentration. This activity is part of the Svalbard Integrated Arctic Earth Observing System (SIOS), which aims to monitor the impacts of climate change, such as the rapid loss of sea ice cover, the retreat of local glaciers, and the Atlantification of Arctic seas. Time series acquisition is ongoing and will continue, supported by funding from JRA ENI-CNR. The project's goal is to analyse the environmental feeback related to the material released into the marine environment due to permafrost melting. Reactivated permafrost can have significant consequences for both climate and the environment by contributing to the release of greenhouse gases into the atmosphere and pollutants into aquatic ecosystems.
-
Freshwater input in the Kongsfjorden (FIKO) Project Start: 2010-06-01 End:2020-12-31 FIKO project aims to acquire measurements of the chemical and physical characteristics of water masses in Kongsfjorden, and estimate the amount of fresh water released from glaciers, in order to study the interactions of this water with the warmer Atlantic waters. The dataset consist of water column profiles of pressure, temperature, salinity, fluorescence and turbidity located within the Kongsfjorden at Platform: MS Teisten - Kings Bay AS, vertical resolution 0.5 m Kongsfjorden_CTD_profiles_2013: 48 water column profiles by SBE19plus CTD probe Kongsfjorden_CTD_profiles_2014: 42 water column profiles by SBE19plus CTD probe Kongsfjorden_CTD_profiles_2015: 82 water column profiles by SBE19plus CTD probe Kongsfjorden_CTD_profiles_2016: 34 water column profiles by SBE19plus CTD probe Kongsfjorden_CTD_profiles_2017: 5 water column profiles by SAIV A/S SD204 – CTD/STD Kongsfjorden_CTD_profiles_2018: 41 water column profiles by SAIV A/S SD204 – CTD/STD Kongsfjorden_CTD_profiles_2019: 12 water column profiles by SAIV A/S SD204 – CTD/STD Kongsfjorden_Krossfjorden_CTD_profiles_2020: 29 water column profiles by SBE19plus CTD probe in 3 different areas: Krossfjorden, kongsfjorden at one transect along the fjord axis, off Bayelva river area.
-

Time series of marine particles fluxes and its compositions (Time and spatial scale: 15-90 days, fixed depth 83 m, 17 m above bottom). Flux of total mass, TMF, (g m-2 day-1) - Organic Carbon, OC, (per cent) - Calcium carbonate,CaCO3, (per cent) - Biogenic silica, Opal, (per cent) - Lithogenic material, Litho, (per cent) - Delta 13C, d13C, (per mil)
-
Timeseries recorded at the mooring S1, at nominal depth of 1000 m during different deployments. The scope of the measurements is to study the temporal variability of the thermohaline properties of the Norvegian Deep Water, and assosiated deep flow
-
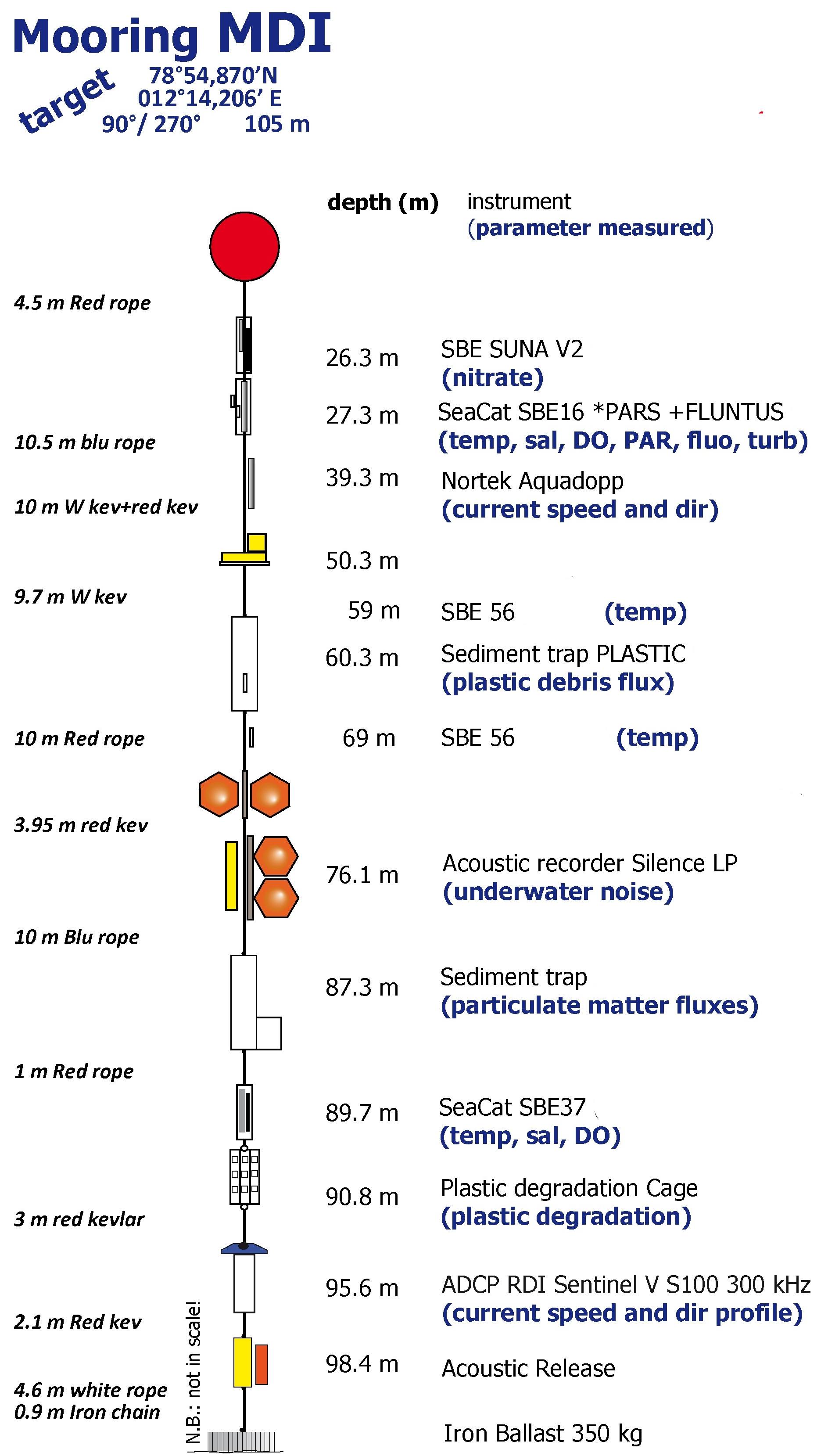
The Mooring Dirigibile Italia (MDI), operated by the Institute of Polar Sciences of the National Research Council (CNR), has been active in the Kongsfjord of the Svalbard archipelago since September 9, 2010. The mooring line is equipped with various instruments placed at depths ranging from 30 to 90 meters in the water column. These instruments collect a wide range of physical and biogeochemical Essential Ocean Variables, including seawater pressure, temperature, conductivity, currents, dissolved oxygen concentration, PAR, fluorescence, turbidity, particle fluxes, nutrients, and ocean sound. This activity is part of the SIOS (Svalbard Integrated Arctic Earth Observing System), designed to monitor the impacts of climate change, such as the rapid loss of sea ice cover, the retreat of local glaciers, and the Atlantification of Arctic seas. Time series acquisition is ongoing and will continue, supported by the integration of this infrastructure into the Italian Marine Data Portal, developed under the ITINERIS PNRR project. This project also funds the enhancement of the research infrastructure with new sensors to improve measurement resolution, expand the number of EOVs measured, and support the continuous collection of long-term data. These efforts will further deepen our understanding of the observed environmental changes.
-
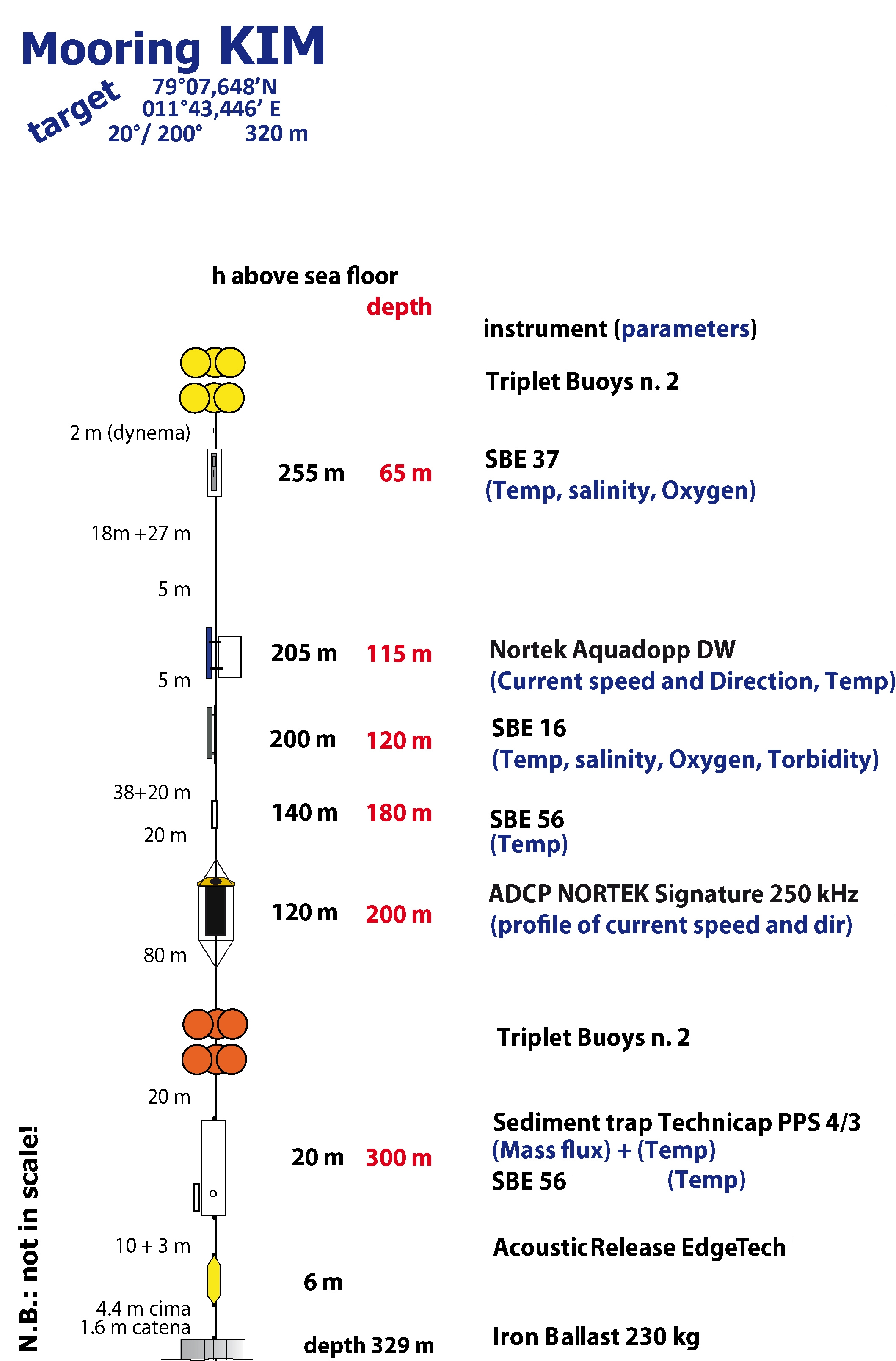
The Krossfjord Italian Mooring (KIM), operated by the Institute of Polar Sciences of the National Research Council (CNR), has been active in the Krossfjord of the Svalbard archipelago since September 9, 2020. The mooring line is equipped with various instruments placed at depths ranging from 65 to 300 meters in the water column. These instruments collect a wide range of physical and biogeochemical Essential Ocean Variables, including seawater pressure, temperature, conductivity, currents, dissolved oxygen concentration, turbidity, particle fluxes and ocean sound. This activity is part of the SIOS (Svalbard Integrated Arctic Earth Observing System), designed to monitor the impacts of climate change, such as the rapid loss of sea ice cover, the retreat of local glaciers, and the Atlantification of Arctic seas. Time series acquisition is ongoing and will continue, supported by the integration of this infrastructure into the Italian Marine Data Portal, developed under the ITINERIS PNRR project. This project also funds the enhancement of the research infrastructure with new sensors to improve measurement resolution, expand the number of EOVs measured, and support the continuous collection of long-term data. These efforts will further deepen our understanding of the observed environmental changes.